Hoe kunnen we helpen?
Disable Energy-Efficient Ethernet in Windows
If you use Ethernet for your connection to internet and/or network equipment and you’re experiencing connection dips or disconnections (especially with consistent but low amounts of throughput), it’s worth checking if your network card is running on Energy-Efficient Ethernet. This networking standard aims to save energy, but it’s not always implemented well in network drivers. Therefore, it can sometimes cause imperfections in performance.
If you want to find out if your network card uses Energy-Efficient Ethernet (and if you’d like to turn it off), keep reading.
Prerequisites
This article assumes:
- your computer is running Windows Vista or newer;
- the affected connection is a wired Ethernet connection. Therefore, your wifi must be turned off when the problems occur for EEE to be a problem.
Steps to take
Estimated time: 5 minutes
Disabling Energy-Efficient Ethernet in Windows:
- Open the Windows Device Manager.
In Windows 10, you can right-click the Start button and choose it from the list that appears.
In earlier versions of Windows, you can reach the Device Manager through Control Panel > System. - Find your network card and open its properties.
Click the arrow at the left of “Network adapters”.
Right-click your wired network adapter and choose “Properties”. - Click the “Advanced” tab at the top of the window.
A big list appears with features of your network adapter. Look for options like Energy-Efficient Ethernet, Power Saving Mode, etcetera. Different adapters will have different names for this.
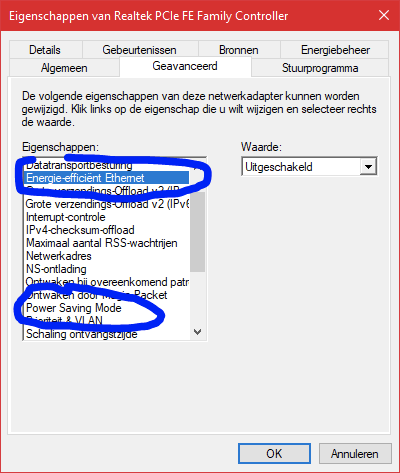
- Disable all energy related options you found in step 3.
Select an option in the list on the left, then choose ‘Disabled’ as the value in the list on the right. Repeat for every option you’d like to modify.
- If it exists: go to the “Advanced” tab and disable all energy related options here.
- Click OK.
Your network connection will temporarily disappear, and reconnect about 5-15 seconds later.
If your NIC’s built-in power saving was indeed the culprit, the problems should now be gone.

